Proportion of children vulnerable in at least one domain of the EDI who are vulnerable in language and cognitive development, at age 5, select provinces/territories, Canada, 2007 to 2012 for selected years
Notes:
*Provincial/territorial analysis is available for only those jurisdictions that have complete province-/territory-wide coverage and have participated in this analysis.
Data Years: P/T Data collection Period
PE 2007-2008
NB 2008-2009
QC 2011-2012
ON 2009-2010 to 2011-2012
MB 2010-2011
SK 2008-2009 to 2010-2011
BC 2009-2010 to 2010-2011
YT 2011-2012
NT not available
Source: CICH graphic created using data adapted from Canadian Institute for Health Information. Children Vulnerable in Areas of Early Development: A Determinant of Child Health. Ottawa, ON: CIHI; 2014.
https://secure.cihi.ca/free_products/Children_Vulnerable_in_Areas_of_Early_Development_EN.pdf -accessed July 24, 2017.
The Language and Cognitive Development domain of the Early Development Instrument (EDI)** includes reading awareness, age-appropriate reading and writing skills, age-appropriate numeracy skills, ability to understand similarities and differences, and ability to recite back specific pieces of information from memory.
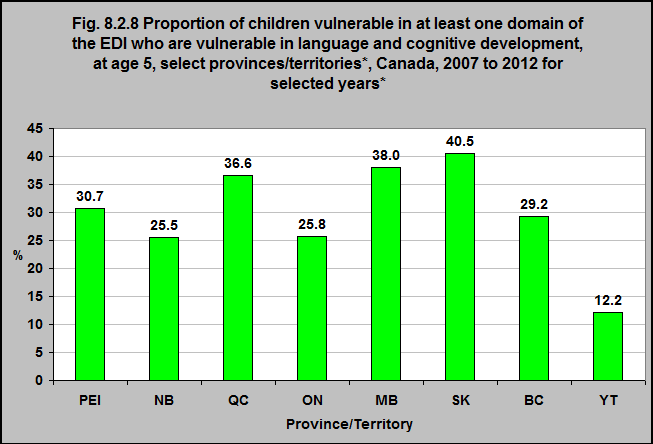
40.5% of all children in Saskatchewan who are vulnerable in at least one area of the EDI are vulnerable in language and cognitive development.
12.2% of the children in the Yukon who are vulnerable in at least one area of the EDI are vulnerable in language and cognitive development.
There are differences between how the EDI is administered between provinces and territories, as well as differences in how often it is administered. Therefore, the time period is not uniform – this needs to be considered when looking at differences across province/territories.
**For more information on the Early Development Instrument (EDI) please click here
