Public spending on family benefits in cash, services, and tax measures, in per cent GDP, 2007
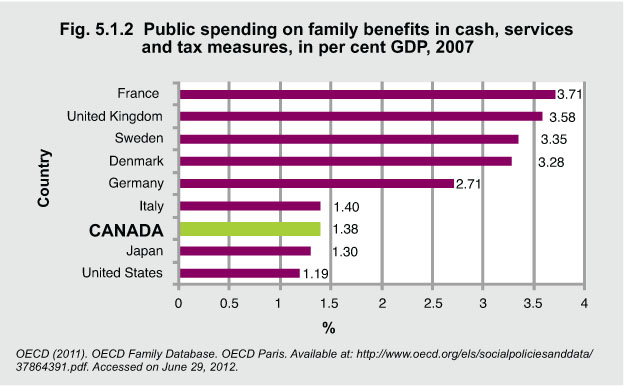
Public spending on family benefits includes financial support that is exclusively for families and children. The OECD* family database includes three types of public spending on family benefits.
1) Child-related cash transfers to families with children. For example, public income support payments during periods of parental leave.
2) Public spending on services for families with children. For example, direct financing and subsidizing of providers of child care and early education facilities.
3) Financial support for families provided through the tax system. For example, child tax allowances.
Public spending on family benefits is an indicator of a government’s commitment to children. OECD countries spend on average 2.2% of their GDP on family benefits. In 2007, France, the United Kingdom, and Sweden spent the highest percentage of GDP, followed by Denmark. These countries spent between 3.2% and 3.7% of GDP on children and families, more than twice as a much as Canada at 1.3%.
* OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) is an organization that acts as a meeting ground for 30 countries that believe strongly in the free market system.
