Categories of substantiated child maltreatment, Canada, 2008
Source: CICH graphics created using data adapted from the Canadian Incidence Study of Reported Child Abuse and Neglect, 2008. http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/cm-vee/csca-ecve/2008/assets/pdf/cis-2008_report_eng.pdf – accessed July 21, 2017.
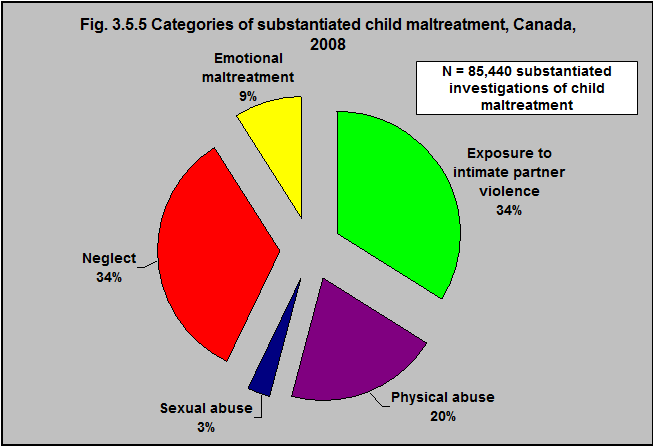
According to the Canadian Incidence Study of Reported Child Abuse and Neglect1, there were over 85,000 substantiated investigations of child maltreatment/neglect in Canada in 2008.
34% were neglect and 34% were exposure to intimate partner violence.
20% were physical abuse.
8% of all substantiated investigations were of children under 4 and 26% among 4 to 7 year olds.1
1Canadian Incidence Study of Reported Child Abuse and Neglect, 2008. http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/cm-vee/csca-ecve/2008/assets/pdf/cis-2008_report_eng.pdf-accessed July 21, 2017.
Implications
The consequences of child abuse and neglect can be devastating and long term. The impact can include physical, psychological, behavioural and societal consequences – and a combination of all of them. While not all children suffer serious long-term effects, the impact on the child will be dependent on their age/developmental stage; they type of maltreatment; the frequency, duration and severity of the abuse; and the relationships of the abuser to the child. It is imperative for communities to provide both prevention approaches and services as well as protect children, support them and offer treatment for the effects of the abuse.2
2Child Welfare Information Gateway. Long-Term Consequences of Child Abuse and Neglect. Factsheet. 2013 https://www.childwelfare.gov/pubPDFs/long_term_consequences.pdf -accessed July 26, 2017.
